Generalized Anxiety Disorder Treatment Center

Studies show that as many as 6.1 million people, or 3.1% of the US population, are struggling with GAD. Along with interfering with everyday life, it does not have any specific triggers. As the name implies, people with this condition have a general concern about various aspects surrounding them. They could be worried about their health, family, financial situation, or even something as mundane as the weather.
Since most individuals struggling with the condition are unable to control their worry, they might think that there is no way to reduce the symptoms of GAD. Fortunately, different treatments for GAD exist, and this quick guide looks at all of the information that you need to know about Generalized Anxiety Disorder.

The Nature of GAD
GAD, unlike other forms of anxiety, does not have any clear triggers or causal explanations. Although it can likely develop as a result of trauma, there are no specific or consistent triggers. So even if an individual can isolate themselves from something that was initially triggering them, it is possible that something in their new vicinity will also have the same effect.
As a result of GAD’s unique nature, treatment for the condition does not focus on helping people overcome their triggers. Instead, therapists will often focus on alleviating symptoms by addressing the core issues underneath.
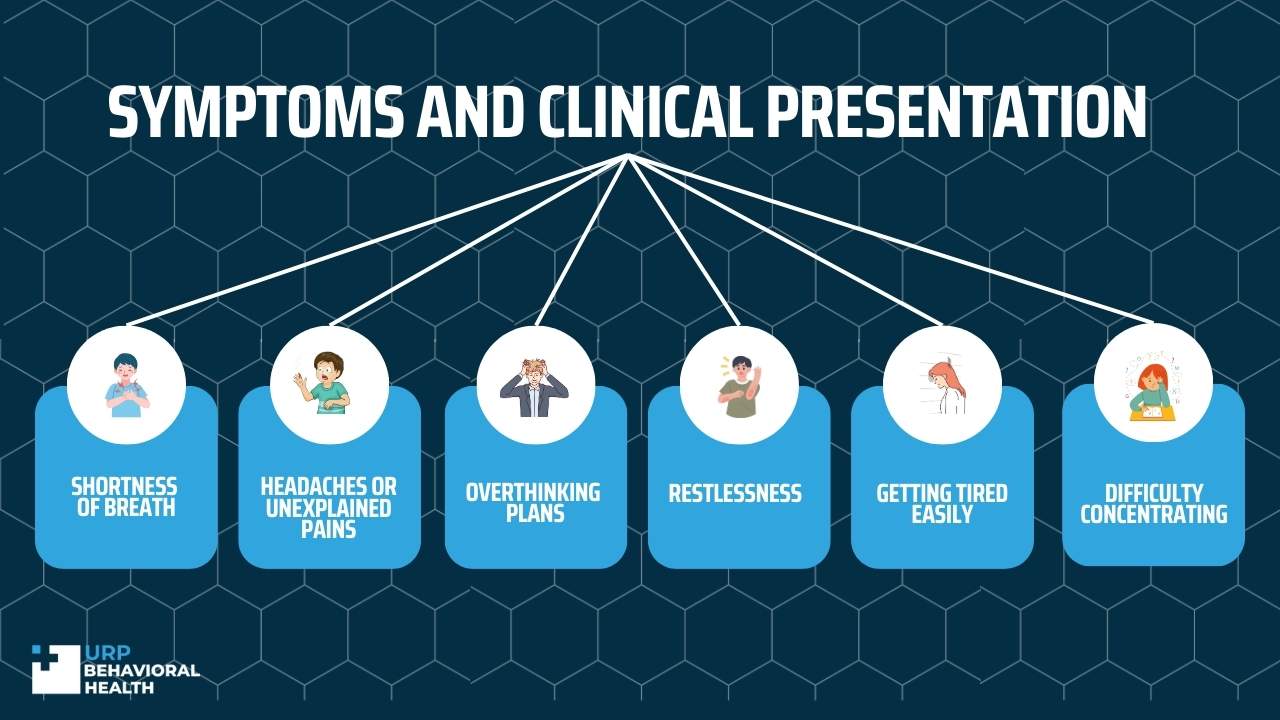
Symptoms Generalized Anxiety Disorder and Clinical Presentation
Shortness of breath: GAD can cause stress, which can create a tightness in your chest, making it hard to breathe. Shortness of breath can result in less oxygen going to the brain, causing panic, increasing anxiety, and making it even harder to breathe.
Headaches or unexplained pains: Headaches are one of the first signs that doctors often look for when performing a GAD diagnosis, as stress can cause the muscles to tense up.
Overthinking plans: People with GAD will often overthink situations or plans, often preparing themselves for the worst situation, or will even get worried when they see no exit to a given place.
Restlessness: Restlessness is a common symptom in generalized anxiety disorder, as the constant stress can make it difficult to relax, often causing shortness of breath.
Getting tired easily: constant worrying and overthinking can often result in mental fatigue, which means that they are not as productive, which can induce anxiety.
Difficulty concentrating: As a restless mind wanders through different hypotheticals, it can be difficult to focus and stop worrying about relatively mundane things.
Causes and Underlying Factors
Genetics: Parents struggling with anxiety or any other mental health concerns can often pass down their symptoms to their children. Studies show that moderate familial aggregation is possible.
Early Years and Upbringing: Certain experiences during people’s formative years can result in them developing GAD, such as growing up in an abusive home or regularly being stressed as a child.
Unique brain function and chemistry: Studies suggest that individuals who have fewer connections between the emotional and logical sides of their brains can develop GAD.
Traumatic experiences: Traumatic experiences are often the biggest indicator of anxiety and related disorders, as they are unable to process their traumatic experiences effectively.
Struggling with a chronic illness: People struggling with a chronic illness that was not a direct result of their actions can develop GAD as they fear other factors out of their control.
Being in a stressful environment: Other than being in a stressful environment at the office, a stressful home or school environment often contributes to people developing GAD.
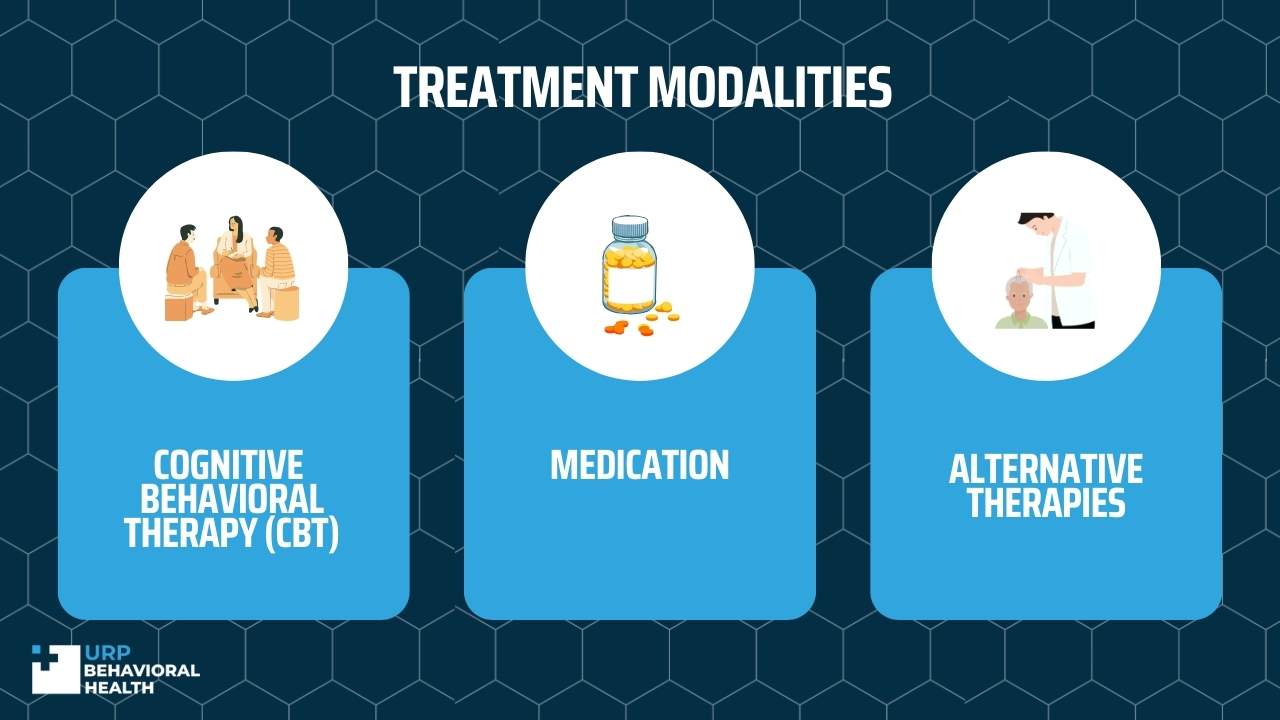
Treatment Generalized Anxiety Disorder
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
It is one of the most popular forms of treatment for Generalized Anxiety Disorder. It is a type of psychotherapy that explicitly focuses on teaching you relevant skills to help you better manage symptoms of anxiety.
CBT is also very effective at helping people get back into their daily routines, helping them resume activities that they had left behind because of their anxiety. One of the subtypes of CBT is trauma-focused CBT, which can dive deeper into traumatic experiences that people have experienced and how to come to terms with them. CBT does not just help people of all ages; it is one of the most tested treatment options for anxiety.
Medication
Another popular form of treatment for Generalized Anxiety Disorder is medication. Medication helps relieve some of the more severe physical and mental symptoms that come as a result of anxiety. Headaches, chest pains, tensing muscles, and increased stress are just some of the symptoms that different types of medication can help relieve.
- Benzodiazepines: These are very potent muscle relaxants that can immediately help calm the body and mind. They are often given in limited quantities and are especially helpful when people are struggling with panic attacks. The only downside to them is that they can be addictive.
- Antidepressants: Antidepressants are another effective way to help reduce the symptoms of anxiety, but they are often given in the long run. Some medicines can even take a few days or weeks to start showing desired effects.
Alternative Therapies Generalized Anxiety
Medication and CBT are not always very effective for people struggling with GAD. Sometimes, these people will require consistent supervision and a routine to follow to develop healthier habits and coping mechanisms. Residential inpatient treatment programs can go a long way in helping you feel more at ease with your surroundings.
You will be around trained professionals who know how to handle symptoms of anxiety best, as well as a more calming environment. There will also be regular sessions with your therapist, which can make it a lot easier to heal from past traumas.
Conclusion
Generalized Anxiety Disorder can be difficult to live with, as people will rarely understand why they find certain things in their environment triggering. And despite some symptoms making it difficult to complete day-to-day tasks, different treatment options do exist. Not only can they help ease the symptoms you are experiencing, but you can also come to terms with traumatic experiences in your life.
Let Us Guide You Towards Healing
We know that seeking treatment can be overwhelming, but our staff is here to make the process as smooth as possible. We’re available 24/7 to address any questions or concerns you may have.

