Borderline Personality Disorder and Bipolar Disorder Treatment Center

Borderline personality disorder vs bipolar disorder are two conditions that may appear similar due to symptoms like impulsivity and extreme mood shifts. But despite being two different conditions, misdiagnosis is common. According to one study, 40 percent of people who met the criteria for BPD were misdiagnosed with bipolar disorder.

What is Bipolar Disorder?
Bipolar disorder is a class of mood disorders characterized by extreme mood disturbances in the form of manic, hypomanic, and major depressive episodes. Bipolar I disorder involves manic and depressive episodes, though only a manic episode is required for a diagnosis. Meanwhile, bipolar II disorder involves hypomanic and depressive episodes, both of which are required for a diagnosis. With professional guidance and treatment like inpatient treatment at URP Behavioral Health, you’ll start to see a change in symptoms.
Symptoms of Bipolar and Borderline Personality Disorder
Symptoms of Bipolar Disorder and Borderline Personality Disorder (BPD) can overlap, making diagnosis challenging.
Bipolar Disorder is characterized by extreme:
- mood swings, including manic episodes with elevated mood;
- increased energy;
- impulsivity;
- depressive episodes marked by sadness, low energy, and hopelessness.
Borderline Personality Disorder involves:
- intense emotional instability;
- fear of abandonment;
- impulsive behaviors;
- unstable relationships.
Individuals with BPD may also experience mood swings, but these are typically more rapid and triggered by interpersonal conflicts. Recognizing the distinct and overlapping symptoms of these disorders is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment, ensuring better management of both conditions.
Similarities Between Bipolar Disorder and BPD
To an outsider, the symptoms of bipolar disorder and BPD may appear similar. That’s because a few of them overlap, such as:
- Acting impulsively and making decisions without thinking them through
- Having low self-esteem and self-worth
- Experiencing extreme changes in mood
- Engaging in self-destructive behaviors that can have painful consequences, like substance abuse
- Having suicidal thoughts or engaging in self-harm behavior
- Having strained relationships with loved ones
Nevertheless, both of these are from completely different categories requiring different criteria for diagnosis and treatment options.
Treatment For Bipolar Disorder and Borderline Personality Disorder in URP Behavioral Health
At URP Behavioral Health, we create a supportive environment specifically designed to support recovery from bipolar disorder and borderline personality disorder (BPD). Our facility offers a peaceful setting with comfortable living quarters, quiet indoor retreats, a dedicated Zen room for quiet reflection, and safe outdoor areas for relaxation. Recreational activities such as basketball and the nature around us promote physical health and personal growth.
Our compassionate and qualified staff is available 24/7, providing continuous support and supervision. Family therapy sessions are conducted with the participation of loved ones to improve communication and create a supportive home environment. Educational programs provide patients and their families with the knowledge they need for effective management.
Choosing URP Behavioral Health means access to a supportive, safe, and calm environment dedicated to your recovery and growth.
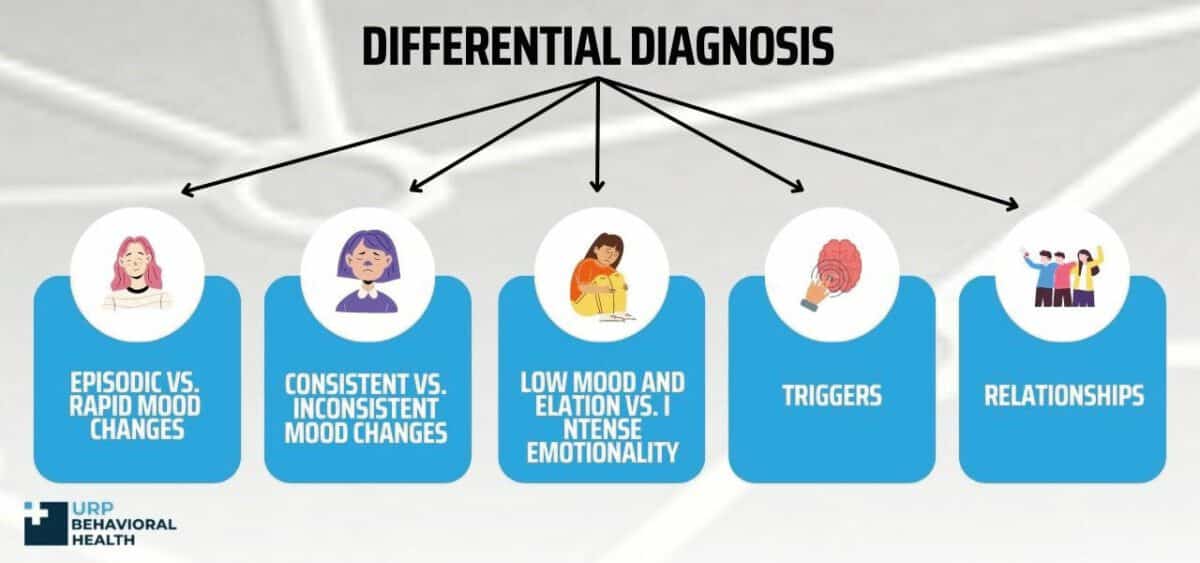
Differential Diagnosis
Episodic vs. Rapid Mood Changes
Although both disorders show mood changes, the nature of these shifts is distinct. In bipolar disorder, you experience episodic mood disturbances in the form of mania and depression. On the other hand, BPD causes intense feelings of anger, loneliness, and desperation.
Consistent vs. Inconsistent Mood Changes
Your therapist will also look at the timeline of your mood changes. Mood episodes in bipolar disorder last for a few days, at the very least. That means you’ll experience consistently low or elevated mood for the entire period of time. But in BPD, mood shifts occur for shorter periods, lasting only a few hours at a time.
Low Mood and Elation vs. Intense Emotionality
In BPD, mood changes rarely involve feeling elated. Elevated mood is commonly associated with bipolar disorder, where your mood shifts from feeling sad and hopeless to euphoric and elated.
Triggers
In BPD, how people treat you has a major effect on how you feel. This is especially when you think that someone will abandon you. Real or perceived abandonment can lead to intense emotions of anger and fear. This can also result in self-destructive behaviors and even self-harm. In bipolar disorder, it’s possible that mood shifts occur due to stress, but they can occur due to no reason as well.
Relationships
While both disorders can put a strain on relationships, BPD leads to an intense fear of abandonment, which affects your ability to have stable relationships. When you have BPD, your feelings for people may go from extreme to dislike. Although mood changes associated with bipolar can cause difficulties in relationships, there’s no fear of abandonment.
Therapy BPD and Bipolar
URP Behavioral Health offers specialized therapy methods for individuals with Borderline Personality Disorder (BPD) and Bipolar Disorder. Our approach includes cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) to help patients identify and change negative thought patterns, and dialectical behavior therapy (DBT) to teach skills in emotional regulation, distress tolerance, and interpersonal effectiveness.
Individual therapy sessions provide personalized support, addressing specific challenges and developing effective coping strategies. Group therapy fosters a sense of community and mutual support, essential for social skill enhancement. Holistic practices such as mindfulness, meditation, and yoga are incorporated to manage stress and promote overall well-being.
These therapeutic methods, combined with our dedicated and compassionate staff, create a comprehensive and integrative treatment plan aimed at promoting lasting recovery and improving the quality of life for those with BPD and Bipolar Disorder.
Let Us Guide You Towards Healing
We know that seeking treatment can be overwhelming, but our staff is here to make the process as smooth as possible. We’re available 24/7 to address any questions or concerns you may have.

