Types of Schizophrenia
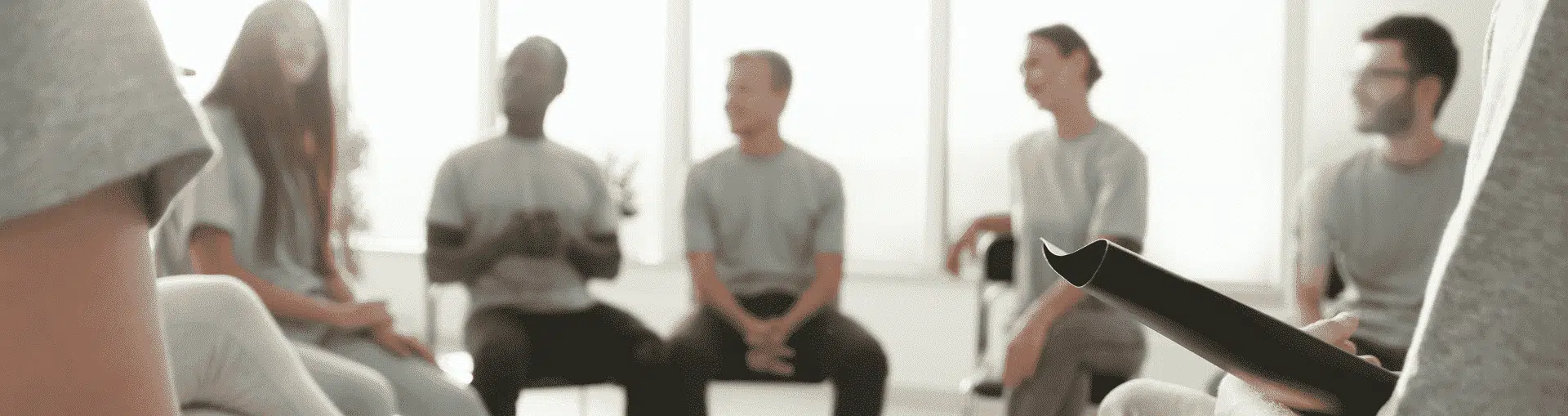
In this article, we are going to take a look at what are the types of schizophrenia disorder. First of all, let us teach ourselves what schizophrenia is generally.
Schizophrenia is a complex and dangerous mental disease that usually is characterized by the following symptoms:
- Hallucinations
- Delusions
- Disorganized thinking
- Lack of motivation
- Slow movement
- Change in sleep patterns
- Changes in body language and emotions
- Trouble focusing
In order to create the most efficient plan of treatment it’s crucial to understand the uniqueness of each type of schizophrenia and reach the best outcomes of curing.
What Are Different Types of Schizophrenia?
Schizophrenia is classified based on the typical symptoms a patient is experiencing. Each type of disorder has unique signs and features that distinguish it from other ones. It’s essential to understand this difference for therapists in order to develop the most efficient treatment approaches and get the best outcomes for their patients [1][2][3].
Our team will verify your insurance and design a plan tailored to your needs.
5 Schizophrenia Types and Symptoms
What are the types of schizophrenia disorder? We’ll break it down below.
Paranoid Schizophrenia
The first type of schizophrenia disorder we are going to learn about is paranoid schizophrenia. Among all, two striking features that make this type are the presence of remarkable delusions and auditory hallucinations. People suffering from this type of disease usually possess the feeling of persecution and grandiosity which leads to serious distress and problems in a daily routine. The curing approach for paranoid schizophrenia often includes antipsychotic medications and cognitive-behavioral therapy [1].
Catatonic Schizophrenia
The catatonic type of schizophrenia manifests through a significant abnormality in the psychomotor behavior of the patient. The patients may experience wild maniacal behaviors or remain completely motionless, which is referred to as catatonic stupor [2].
Disorganized Schizophrenia
Disorganized schizophrenia is the disorganization in the thoughts, speech, and behavior of an individual. A person suffering from this type of schizophrenia also displays a range of emotions that do not fit the circumstances and is often unable to carry out daily activities as expected [3].
Undifferentiated Schizophrenia
Symptoms that do not clearly fit paranoid, catatonic, and disorganized types are undifferentiated schizophrenia. This type applies to those individuals who present with many symptoms and when no symptom predominates. It is often particularly invidious to diagnose and treat, since the patient’s symptoms may be quite varied. Combination treatment is necessary for success in the management of this type of schizophrenia [1].
Residual Schizophrenia
Residual schizophrenia is a type of schizophrenia in which the individual has a history of one or more schizophrenia episodes; however, they do not show important positive symptoms at that instant. In other words, they may show negative symptoms such as flat affect and social withdrawal [2].
Are There Other Subtypes of Schizophrenia?
Even though the five types specified are the main classifications, there are other types of schizophrenia that are still under research. Such types include simple schizophrenia which refers to a gradual deterioration of functioning with no significant positive symptoms and schizoaffective disorder which shows the features of both schizophrenia and mood disorders. The importance of understanding these other types is for a better treatment and care approach [3].
Conditions Related to Schizophrenia
There are many disorders with similar symptoms to schizophrenia and some of them may co-occur with the disorder other than structural features and it has common symptoms. This group consists of schizotypal personality disorder, delusional disorder, and brief psychotic disorder. Some of them may be confused with schizophrenia, so exploring and understanding the difference between them is vital in the diagnosis and treatment of patients suffering from these disorders. Diagnosis and clear distinction of these conditions are important in order to provide the best treatment that is individual for each patient’s needs [1][2].
Reach out today and let us create a treatment plan designed around your needs.
Conclusion
Schizophrenia is a multifaceted condition that can be presented in various forms. Each form is diagnosed based on its own symptoms. For this reason, it is very important for therapists to explore and understand the differences between types in order to provide better treatment strategies for their patients. In the event that any of your relatives or you are experiencing any signs or symptoms that may be similar to any type of schizophrenia, it is very important to get medical attention without delay. Understanding and resolving the condition at an early stage can be beneficial and it can speed up the recovery process and the overall life quality.
Sources
- [1] “Schizophrenia: Overview and treatment options”. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19940542/
- [2] “Diagnosis and classification of schizophrenia”. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7346895/
- [3] “Subtypes of schizophrenia and their treatment”. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20677436/